Human Heart Diagram and Anatomy of the Heart StudyPK
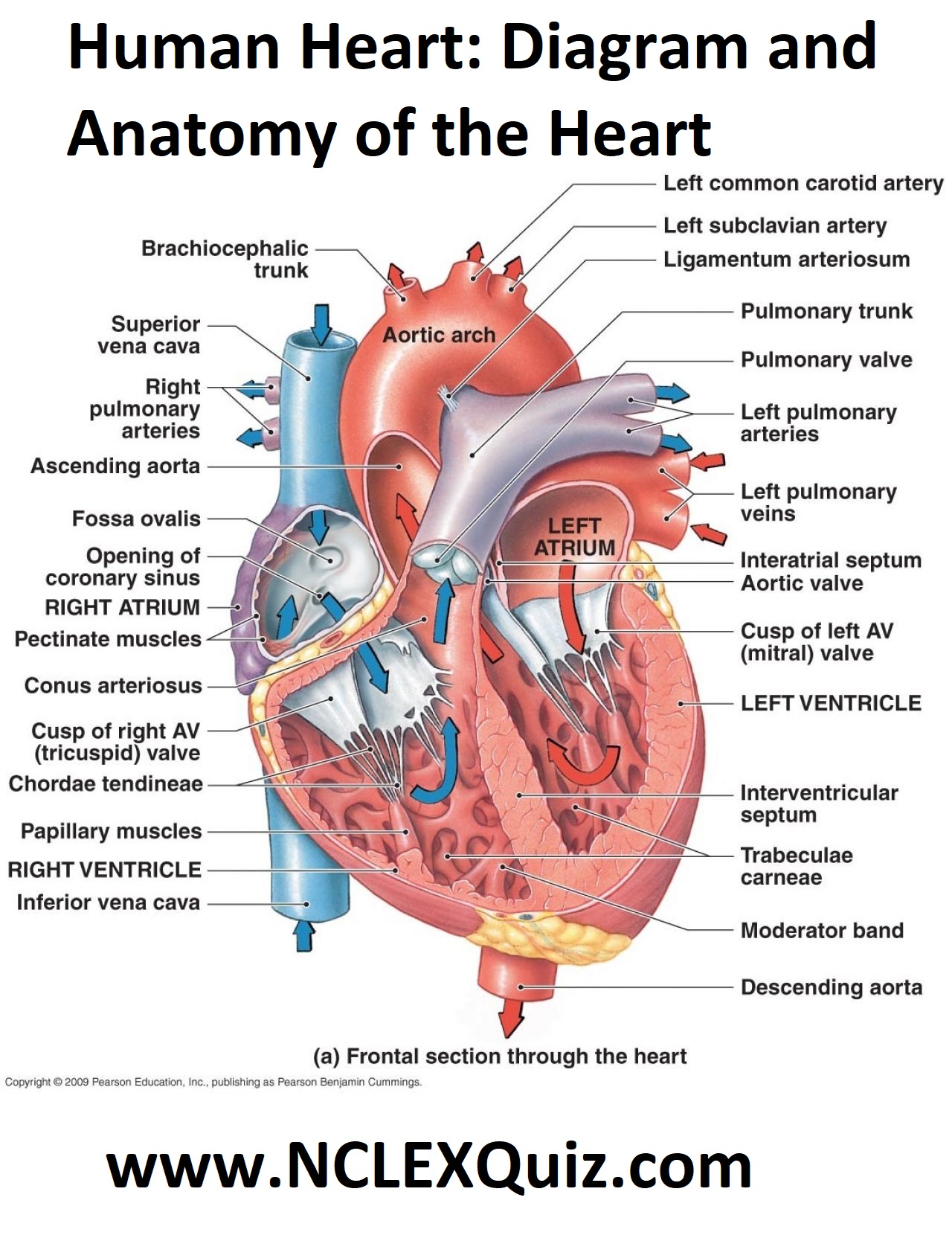
The cardiac skeleton also provides an important boundary in the heart electrical conduction system. Figure 16.4.1 16.4. 1: Internal Structures of the Heart This anterior view of the heart shows the four chambers, the major vessels and their early branches, as well as the valves. The presence of the pulmonary trunk and aorta covers the.

Diagram of the heart Heart diagram, Medical anatomy, Medical school studying
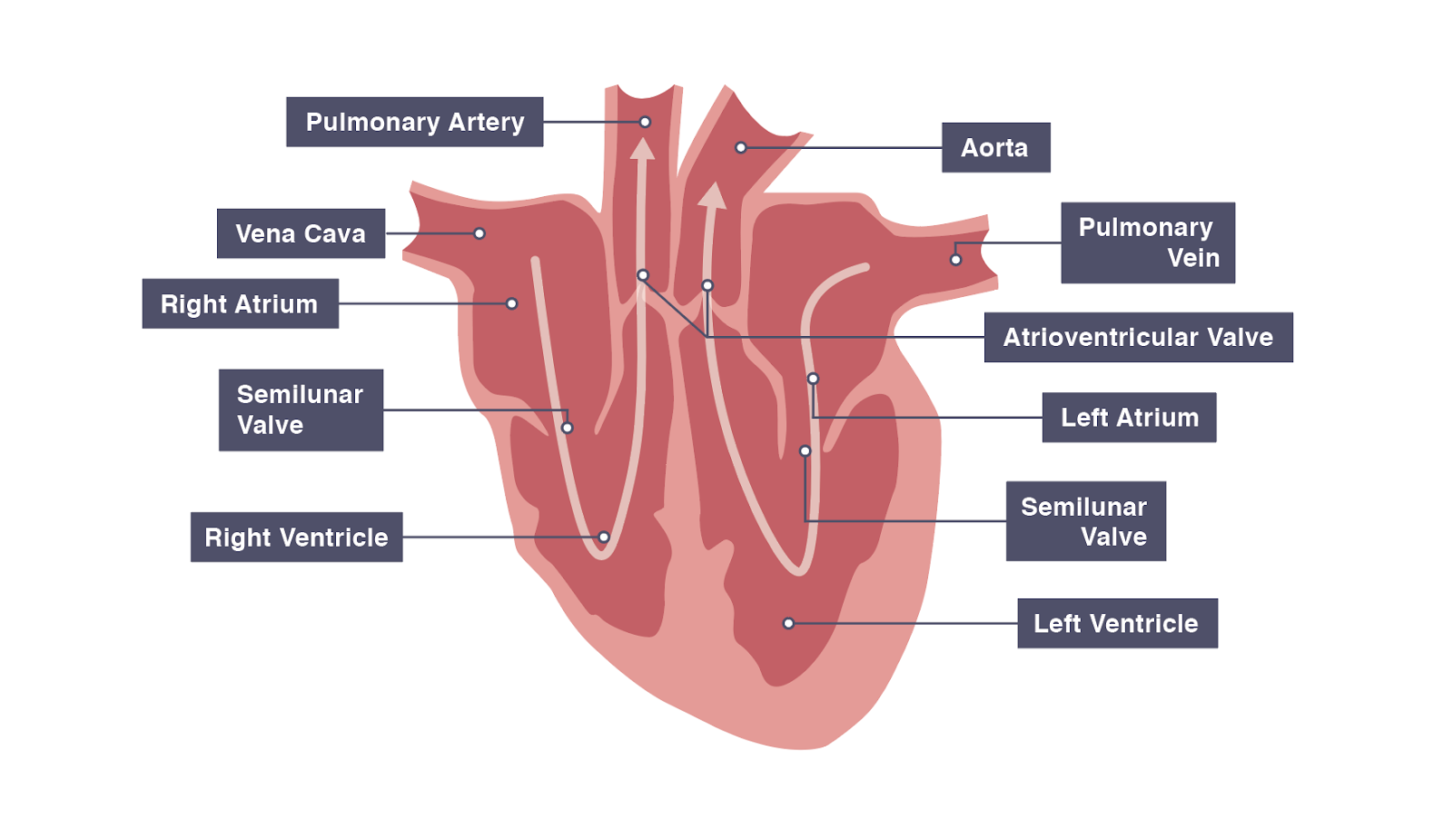
The heart has four chambers. Blood is pumped between the following four chambers: The Circulatory System - Heart: Structure and Function The right and left sides of the heart are divided by a wall called the septum. This ensures that deoxygenated and oxygenated blood don't mix.
/human-heart-circulatory-system-598167278-5c48d4d2c9e77c0001a577d4.jpg)
Flow Of Blood Through The Heart Diagram Photos Idea
The heart is a hollow muscular organ that lies in the middle of the chest cavity. It is enclosed in the pericardium, which protects the heart and facilitates its pumping action. The heart is divided into four chambers: The two atria (auricles): these are the upper two chambers. They have thin walls which receive blood from veins.
Human HeartGross structure and Anatomy Online Biology Notes
The heart is the organ that helps supply blood and oxygen to all parts of the body. It is divided by a partition (or septum) into two halves. The halves are, in turn, divided into four chambers. The heart is situated within the chest cavity and surrounded by a fluid-filled sac called the pericardium. This amazing muscle produces electrical.

iGCSE Biology Gross Structure Of The Heart BioChem Tuition
Diagram of Heart The human heart is the most crucial organ of the human body. It pumps blood from the heart to different parts of the body and back to the heart. The most common heart attack symptoms or warning signs are chest pain, breathlessness, nausea, sweating etc.

External Structures Of The Human Heart
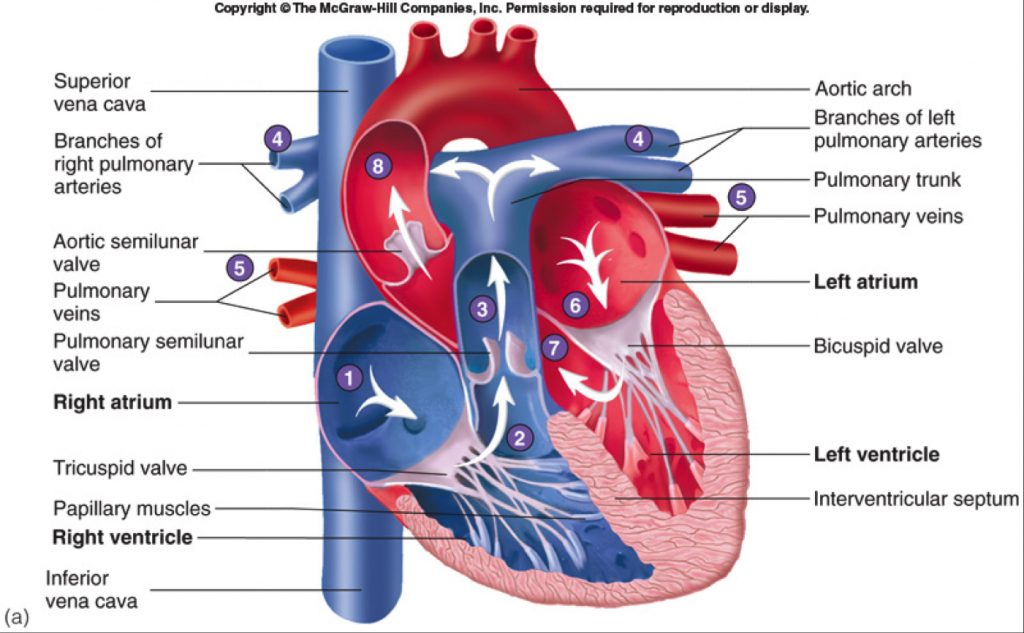
The human circulatory system consists of several circuits: The pulmonary circuit provides blood flow between the heart and lungs. The systemic circuit allows blood to flow to and from the rest of the body. The coronary circuit strictly provides blood to the heart (not pictured in the figure below). Image credit: Blood flow from the heart by.

Cardiac cycle and the Human Heart Grade 9 Understanding for IGCSE Biology 2.65 2.66 PMG Biology
The heart, a hollow muscular organ, is located in the center of the chest. The heart has two sides, right and left. The right and left sides of the heart each have an Atrium: Upper chamber that collects blood and pumps it to the lower chamber Ventricle: Lower chamber, which pumps blood out of the heart
IGCSE Biology Notes 2.63 Describe the Structure of the Heart and How it Functions
In animals with lungs —amphibians, reptiles, birds, and mammals—the heart shows various stages of evolution from a single to a double pump that circulates blood (1) to the lungs and (2) to the body as a whole. In humans and other mammals and in birds, the heart is a four-chambered double pump that is the centre of the circulatory system.

Cardiovascular Disease
The heart is made of three layers of tissue. Endocardium is the thin inner lining of the heart chambers and also forms the surface of the valves.; Myocardium is the thick middle layer of muscle that allows your heart chambers to contract and relax to pump blood to your body.; Pericardium is the sac that surrounds your heart. Made of thin layers of tissue, it holds the heart in place and.
1 Diagram of the human heart. The image depicts the different cavities... Download Scientific
The atria (plural of atrium) are where the blood collects when it enters the heart. The ventricles pump the blood out of the heart to the lungs or around the body. The septum separates the.
IGCSE Biology 2017 2.65 Describe the Structure of the Heart and How it Functions
This video covers the structure and function of the heart, the double circulatory system, the associated blood vessels, pacemaker cells and the coronary arte.
Show a labelled diagram of the heart.
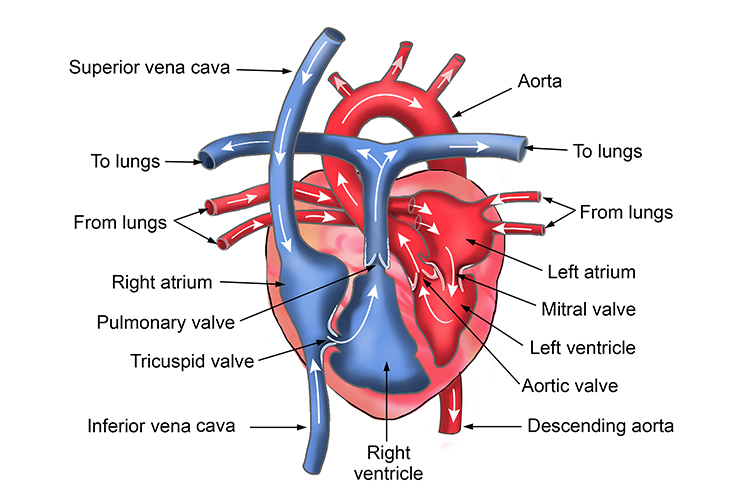
The heart is the control for the circulatory system. It is a muscle that pumps blood around the body. The heart consists of two muscular pumps that lay next to each other. The right side pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs, whereas the left side pumps oxygenated blood to the whole body. There are four chambers in total.
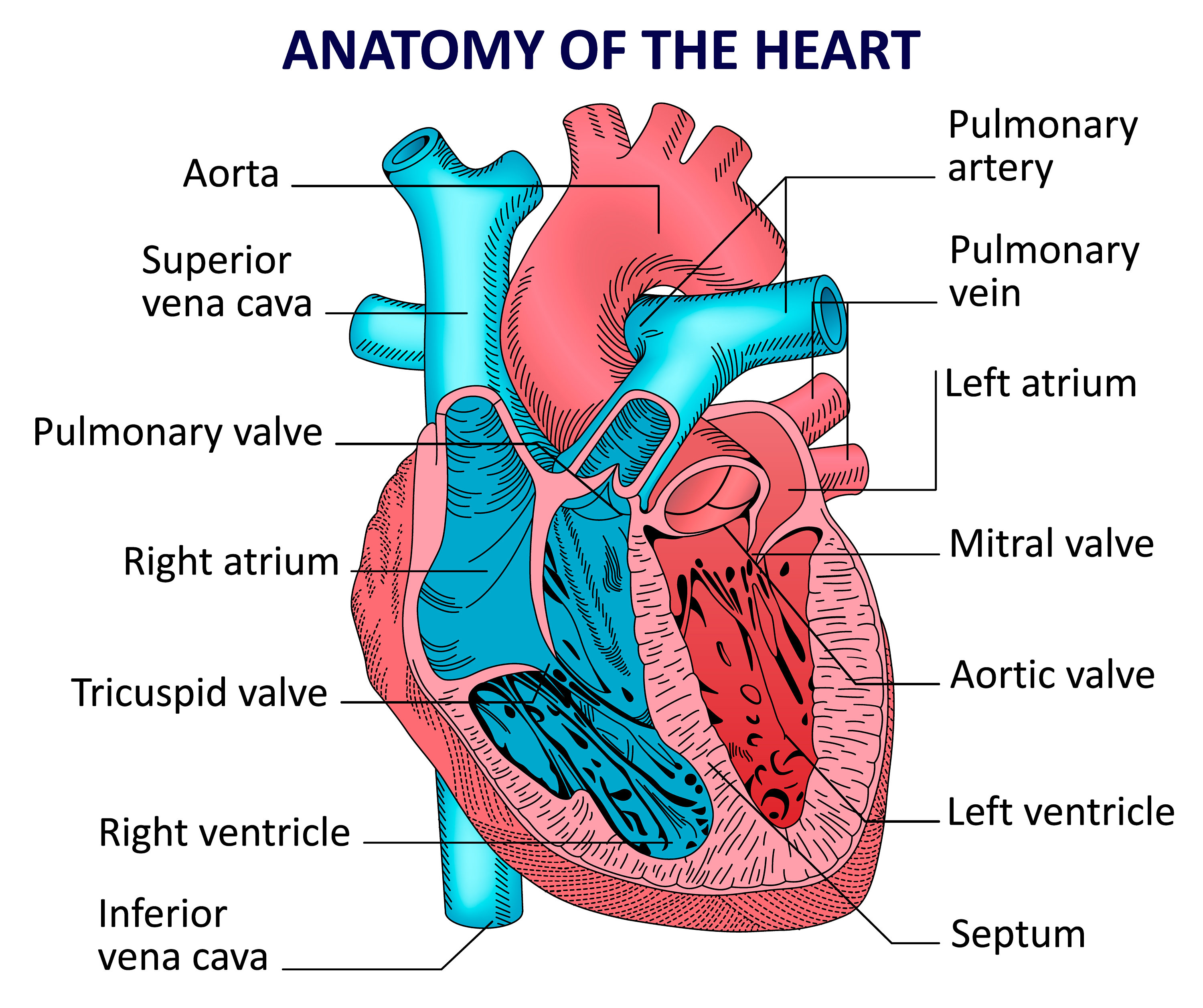
Human heart anatomy. Vector diagram Etsy
. The main parts of the heart, seen in cross-section from the front The blood on the right side of the heart is deoxygenated. It has been around the body and supplied the cells with oxygen.
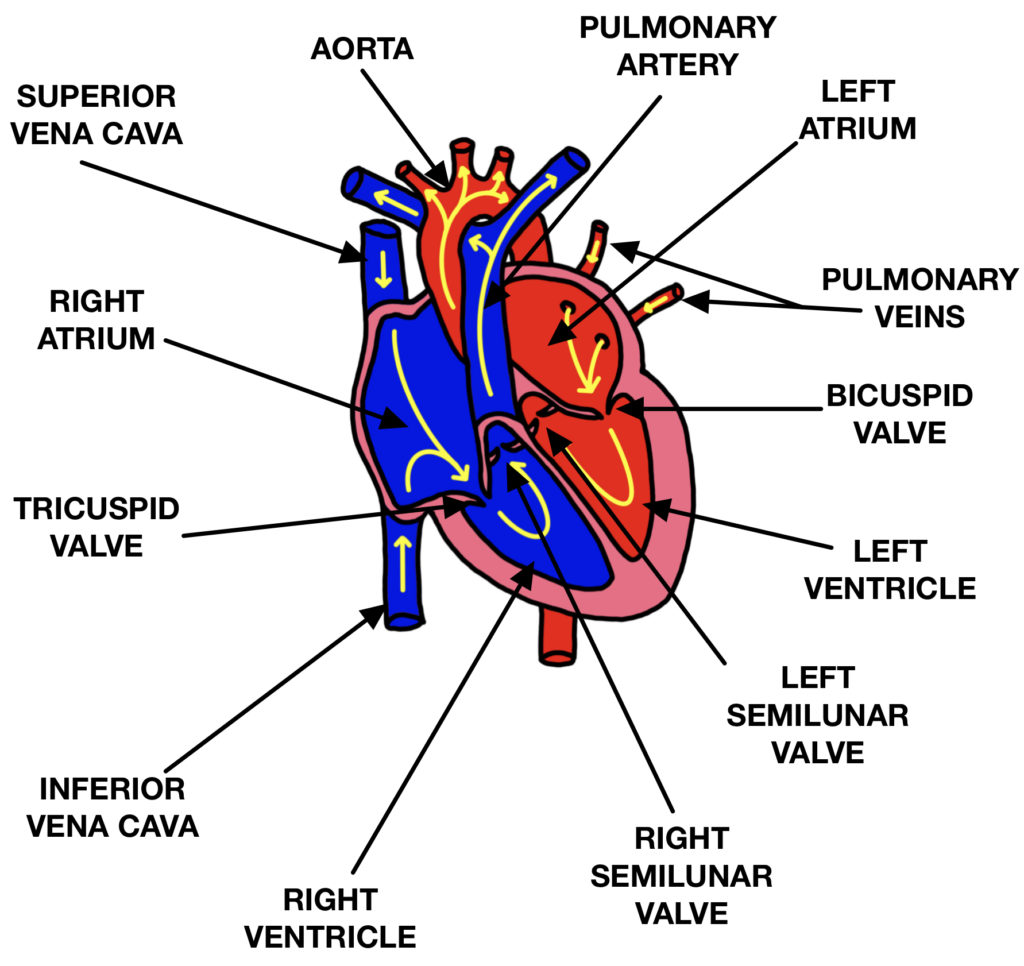
Structure of the Heart The Science and Maths Zone
o Look at the right-hand diagram. Cut carefully upwards into the left atrium along the line shown in the diagram. p Measure and record the thickness of the walls of the atrium and the ventricle. q Examine the right side of the heart in a similar way. r Look at the areas where an atrium joins a ventricle. Examine the structures there.
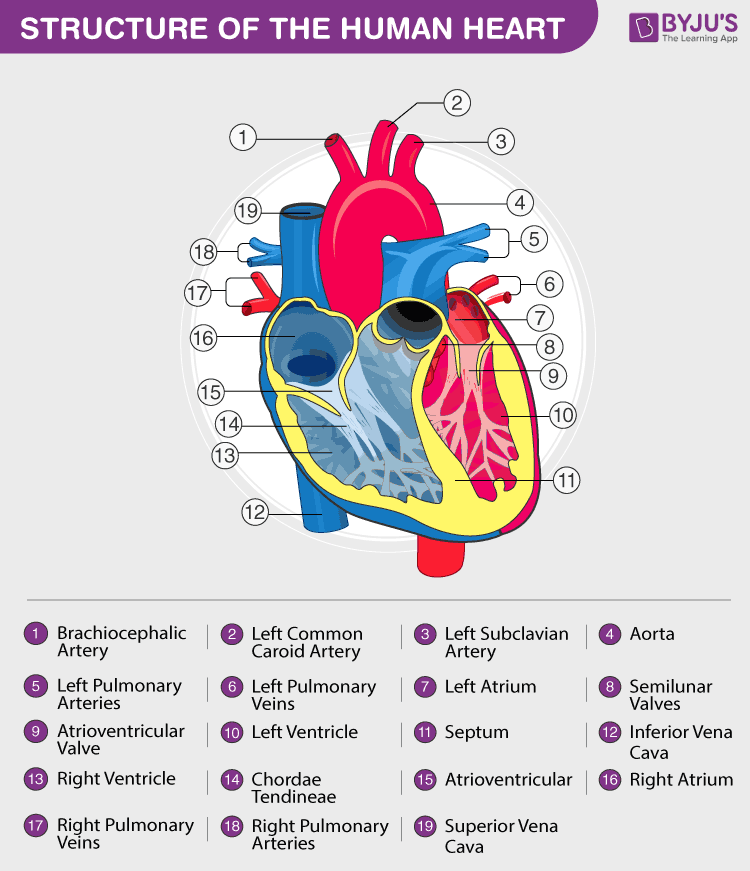
Heart Diagram with Labels and Detailed Explanation
The heart is a unidirectional pump. Valves are present to prevent the backflow of blood. The right side pumps deoxygenated blood (low in oxygen and high in carbon dioxide) to the lungs. The left.

humanheartdiagram Tim's Printables
The heart is labelled as if it was in the chest so what is your left on a diagram is actually the right-hand side (and vice versa) The right side of the heart receives deoxygenated blood from the body and pumps it to the lungs where oxygen diffuses in from the alveoli and carbon dioxide diffuses out